
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a widely adopted protocol that is designed for managing network devices such as routers, switches, servers, network printers, and other network-attached appliances. It enables network administrators to monitor and configure these devices remotely, thereby providing a centralized and efficient approach to network management.
Maintain a comprehensive inventory of your local area network by performing an SNMP scan! Total Network Inventory enables you to build an inventory of your entire network without the need for a complex scanner setup. The SNMP network discovery tool will automatically scan your network for devices and collect detailed information about each router, switch, network printer, and other managed devices in just one pass.
Using the SNMP scanner, network administrators can quickly inventory their network infrastructure, including routers, switches, printers, VoIP systems, and other managed devices.
The SNMP discovery tool in Total Network Inventory offers several benefits:
One of the many powerful features of Total Network Inventory is the ability to check the toner levels of printers on the network. By querying SNMP-enabled printers, the program obtains information about ink or toner levels, allowing administrators to proactively manage printer inventory and maintenance.
In addition, TNI can provide alerts and notifications when the printer toner levels fall below the specified thresholds, which enables administrators to take prompt action and avoid interruptions in printing services.
SNMP network management tools typically provide detailed reports and analysis capabilities in order to help administrators understand and optimize their network infrastructure. TNI offers comprehensive reporting and visualization features:
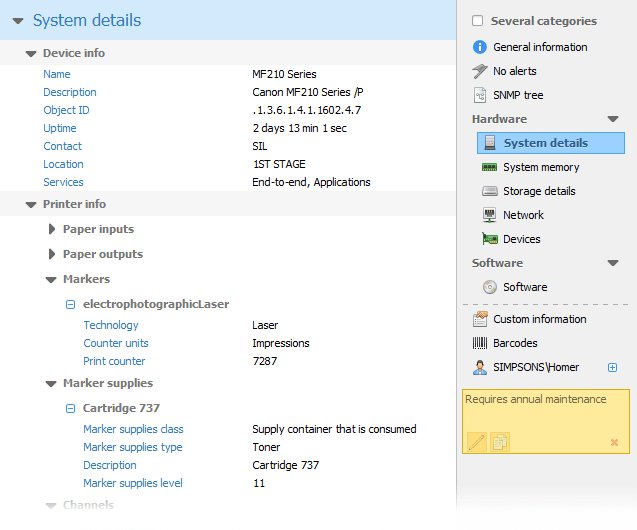
SNMP device discovery software will provide you with important information that will help you identify performance issues with various equipment on your network. Setting up automatic SNMP scanning will help you keep your equipment in good working order as well as detect critical issues before a disaster occurs. Total Network Inventory will help you maintain a well-managed, efficient, and secure network infrastructure for optimizing your IT investments and reducing operating costs.